 |
| What is Computer? |
What is a computer?
A computer is a programmable
electrical device that takes in raw data and processes it with a set of
instructions (a programme) to create the result as output. It produces output
only after conducting mathematical and logical operations and has the ability
to preserve the results for future use. It can do both numerical and
non-numerical computations. The word "computer" comes from the Latin
word "computare," which means to calculate.
The most commonly used full form of
"computer" is "Common Operating Machine Purposely Used for
Technological and Educational Research."
. A computer is designed to run
programmes and deliver a wide range of solutions via integrated hardware and
software components. It uses programmes to operate and expresses decimal
numbers as a string of binary digits. It also has a memory that stores data,
programmes, and processed results. Hardware refers to the components of a
computer, such as cables, transistors, circuits, and hard discs. Software, on
the other hand, refers to the programmes and data.
Charles Babbage is credited with
inventing the first computer, the Analytical Engine, in 1837. As read-only
memory, punch cards were used. Charles Babbage is also recognized as the
computer's father.
History of the computer
Most histories of the contemporary
computer begin with Charles Babbage's Analytical Engine, which was based on the
mathematical theories of George Boole, the mathematician who first expressed
the logic principles inherent in today's digital computer. Ada Lovelace, Babbage's
assistant and colleague, is thought to have developed the concepts of programme
loops and subroutines and is frequently regarded as the first programmer. Apart
from mechanical calculators, the first really usable computers began with the
vacuum tube, which was expedited by the creation of the transistor, which was
subsequently implanted in huge numbers in integrated circuits, allowing the
relatively low-cost personal computer to be realized.
Modern computers are built on the
notion of "stored programmes," pioneered by John von Neumann in 1945.
Essentially, the computer reads the programme one instruction at a time,
performs an action, and then reads the next instruction.
 |
| What is Computer? |
From the mid-1900s until the
present, computer progress has been classified into five generations. While the
time period for each generation varies based on the source, the most widely
accepted generational chronology is shown below.
1940
to 1956
Room-sized devices with vacuum tubes
for circuitry and magnetic drums for limited internal storage comprised the
first generation of computers. For data entry, these computers utilized punched
cards and binary machine code (language). The ABC (Atanasoff Berry Computer),
Colossus, IBM 650, and EDVAC are examples of first-generation computers
(Electronic Discrete Variable Computer).
1956
to 1963
Second-generation computers employed
transistors instead of vacuum tubes, magnetic tape storage for improved storage
capacity, BAL (basic assembler language), and punched cards for input. Transistors
used less energy and produced less heat than vacuum tubes. Second-generation
computers include the IBM 7090, IBM 7094, IBM 1400, and UNIVAC (Universal
Automatic Computer).
1964
to 1971
Third-generation computers used
integrated circuits (ICs) with multiple transistors and MOS (metal oxide
semiconductor) memory. These computers were smaller, cheaper, and quicker than
their predecessors, and they used keyboards for input and monitors for output,
as well as programming languages including FORTRAN (formulaic translation),
COBOL (a common business-oriented language), and C. The IBM 360 and 370 series
are examples of third generation computers.
1972
to 2010
Fourth-generation computers featured
VLSI (very large scale integration) integrated circuits and microprocessors,
RAM (random access memory), ROM (read-only memory), and high-level programming
languages such as C and C++. During this time, the World Wide Web and cloud
computing (the capacity to supply hosted services via the Internet)
significantly improved computer capabilities. Apple's Macintosh and IBM's PC
are examples of fourth generation computers.
2010
and onwards
Fifth-generation computers are AI
(artificial intelligence)-based, with large size integrated circuits and
several CPUs (processors). Fifth-generation computers respond to plain language
input, solve extremely complicated problems, make judgements based on logical
(human-like) thinking, and employ quantum computing and nonmaterial (molecular
manufacturing). Fifth-generation computers and programmes enable numerous
programmes (and computers) to work on the same task simultaneously.
.jpg) |
| What is Computer? |
With the introduction of the
Internet, cloud computing, and fast broadband data transmission, programmes and
data can be distributed quickly and efficiently across a network, while
application programmes and software make computers the preferred tool for word
processing, databases, spreadsheets, conferences, ERP (enterprise resource
planning), simulations, training, CMS (content management systems), gaming, and
engineering.
benefits of using a computer
Increases
productivity:
A computer boosts productivity. For
example, with a rudimentary grasp of a word processor, you can simply and
rapidly write, edit, save, and print documents.
It
connects to the internet by:
allowing you to send emails, read
material, gather information, access social media platforms, and more. You may
connect with long-distance friends and family members by connecting to the
internet.
Storage:
You can store a sizable amount of
data on a computer, including projects, eBooks, papers, videos, images, music,
and more.
Data
and Information Organization:
It not only allows you to store data,
but it also allows you to arrange your data. For instance, you could create
distinct folders to store various kinds of data and information, making it
easier and quicker for you to conduct a search.
enhances
your abilities:
It helps you write better English if
you are not skilled at spelling and grammar. Similarly, if you are not strong
at arithmetic or have a poor memory, you may utilize a computer to conduct
computations and save the answers.
Assist
the physically challenged:
It may be used to assist the
physically handicapped, such as Stephen Hawking, who was unable to talk and
relied on a computer to communicate. By installing specialized software that
enables them to read what is on the screen, it can also help blind people.
keeps
you entertained:
You may use the computer to listen
to music, view movies, play games, and much more.
 |
| What is Computer? |
The computer has become an integral
part of our daily lives. Many of the activities we do in a day are dependent on
a computer. The following are some frequent examples:
Digital
currency:
A computer retains a record of your
activities and account balance, and the money placed in your bank account is
saved as a digital record or digital currency.
Smartphone:
A smartphone is a computer that we use
throughout the day for calling, messaging, and surfing.
ATM:
When you withdraw cash from an ATM,
you are utilizing a computer, which allows the ATM to receive instructions and
issue cash accordingly.
Trading:
Computers are used in stock markets
for day-to-day trading. There are several powerful computer-based algorithms
that manage trading without the involvement of people.
VoIP:
Computers handle and perform all
voice over IP communication (VoIP).
Types of computers
Computers are grouped into three
types: general-purpose computers, special-purpose computers, and specialized
computers.
This article is about
general-purpose computers, which are what most people think of when they think
of computers.
The most frequently used computer is
a special-purpose computer, which is incorporated into practically all
electronic equipment. This type of computer is found in ATMs, vehicles,
microwaves, televisions, VCRs, and other household devices. More information
and examples may be found on our special-purpose computer website.
 |
| Types Of Computer |
A specialized computer, like a
general-purpose computer, is designed to execute only one or a few tasks. For
more information and examples of these computers, see our specialists'
computers.
When you say "computer" or
"PC," you generally mean a desktop computer located in a house or
workplace. However, the distinctions between what makes these machines tick are
becoming increasingly blurred. The following are some instances of what is now
called a computer.
The following is a comprehensive
list of general-purpose computers from the past and present.
Custom-built
PC
Desktop
computer
Thin
client and workstation without a hard drive
Gaming
computer
Hybrid
computer
Notebook,
laptop, portable computer
Mainframe
Microcomputer
Nano
computer
Notebook
PDA
Personal
computer
Prebuilt
computer
Quantum
computer
Server
Smartphone
Stick
computer
Supercomputer
Tablet
Custom-built
PC
Desktop
computer
Thin
client and workstation without a hard drive
Gaming
computer
Hybrid
computer
Notebook,
laptop, portable computer
Mainframe
Microcomputer
Nano
computer
Notebook
PDA
Personal
computer
Prebuilt
computer
Quantum
computer
Server
Smartphone
Stick
computer
Supercomputer
Tablet
Who manufactures computers?
There are two sorts of computers
available today: PCs (IBM compatible) and Apple Macs. Many firms manufacture
and construct PCs, and if you have all of the essential computer parts, you may
even construct a bespoke PC. Apple computers, on the other hand, are designed
and manufactured only by Apple. See our computer businesses page for a list of
firms that manufacture and build computers (OEMs).
Computer connections
Every computer has a unique set of
connections. Our computer connections page has an illustration of the back of a
personal computer as well as brief descriptions of each connection.
What components are required for a computer to
function?
All of the above-mentioned
components are not required for a computer. However, a computer cannot work
without at least the following components:
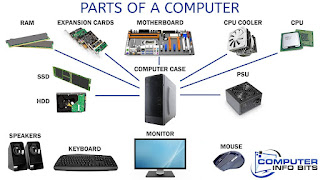 |
| Parts of computer |
Processor:
A component that performs
software and hardware instructions.
Memory:
Memory is the principal
temporary store for data that travels between the storage and the CPU.
Motherboard:
The component that
connects all of the other components
Storage device (e.g., hard drive):
A
slower secondary storage device that keeps data permanently.
However, if you simply possessed the
bare bones of a computer, you would be unable to communicate with it until you
attached at least one input device (e.g., a keyboard). You'd also need at least
one output device (such as a monitor) to observe what's going on.
Related to Computer FAQs
What
is the concise definition of a computer?
A computer is a device that receives
information (in the form of digitalized data) and manipulates it to produce a
result based on a program, piece of software, or set of instructions on how to
process the data.
What
is the best definition of a computer?
a programmable electronic device
that accepts input, performs predefined mathematical and logical operations at
high speed, and displays the results of these processes. Computers of various
sorts include mainframes, desktop and laptop computers, tablets, and smart
phones.
What
are the five different definitions of "computer"?
a type of machine that operates on
data rather than physical objects. (2) Machines that process symbolic
representations of meaning (3) All-purpose devices for doing computations and
data manipulations (4) Data storage, processing, and calculation computers that
can be programmed
What
exactly is a computer introduction?
Computer
Fundamentals:
A computer is an electrical device
that can collect data (input), process the data according to set rules, create
information (output), and store the information for future use.
What
is the full form of a computer?
The most commonly used full form of
"computer" is "Common Operating Machine Purposely Used for
Technological and Educational Research."
Related Articles:

No comments:
Post a Comment